cybersecurity2019

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
On the Use of Max-SAT and PDDL in RBAC Maintenance
This web site contains the dataset and experimental results partially illustrated within the manuscript “On the Use of Max-SAT and PDDL in RBAC Maintenance” which has been submitted to the Cybersecurity journal.
Datasets: Single Exceptions/Violations
SmallComp
Dataset generated by simplyfing the paper working example to obtain optimal solution with a wide range of B values thus enabling the comparison with sub-otpimal solvers
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
| Violation List | viols |
Exceptions: All Max-SAT Formulas
Violations: All Max-SAT Formulas
Domino
Dataset benchmark used in Role-mining literature obtained from the user access profiles of the Lotus Domino Server.
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
| Violation List | viols |
Exceptions: All Max-SAT Formulas
Violations: All Max-SAT Formulas
University
Dataset benchmark used in Role-ming literature generated from a template at the Stony Brook University.
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
| Violation List | viols |
Exceptions: All Max-SAT Formulas
Violations: All Max-SAT Formulas
Firewall1
Dataset benchmark used in Role-ming literature representing policies implemented though firewalls used to provide external users access to internal resources.
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
| Violation List | viols |
Exceptions - Max-SAT Formulas: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21
Violations - Max-SAT Formulas: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21
Selection of a Max-SAT solver
Complete Solvers
| Solver | SmallComp | Domino | University | Firewall1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximo | B<=0.5 | B=0 | B=0 | B=0 |
| MaxHS | B<=0.4 | B=0 | B=0 | - |
| LMHS | B<=0.3 | B=0 | B=0 | - |
| Ahmaxsat | B<=0.25 | - | - | - |
Incomplete Solvers
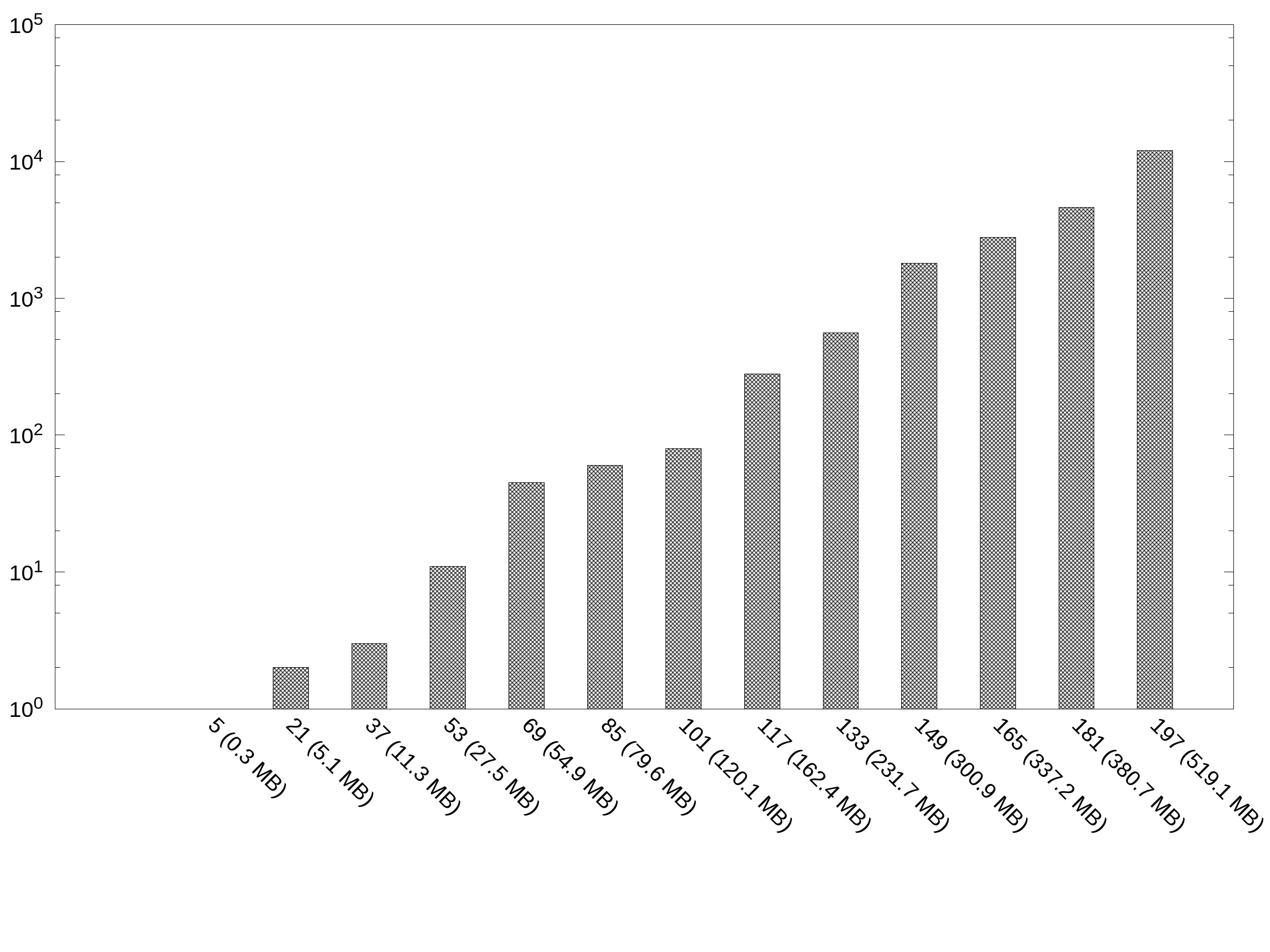
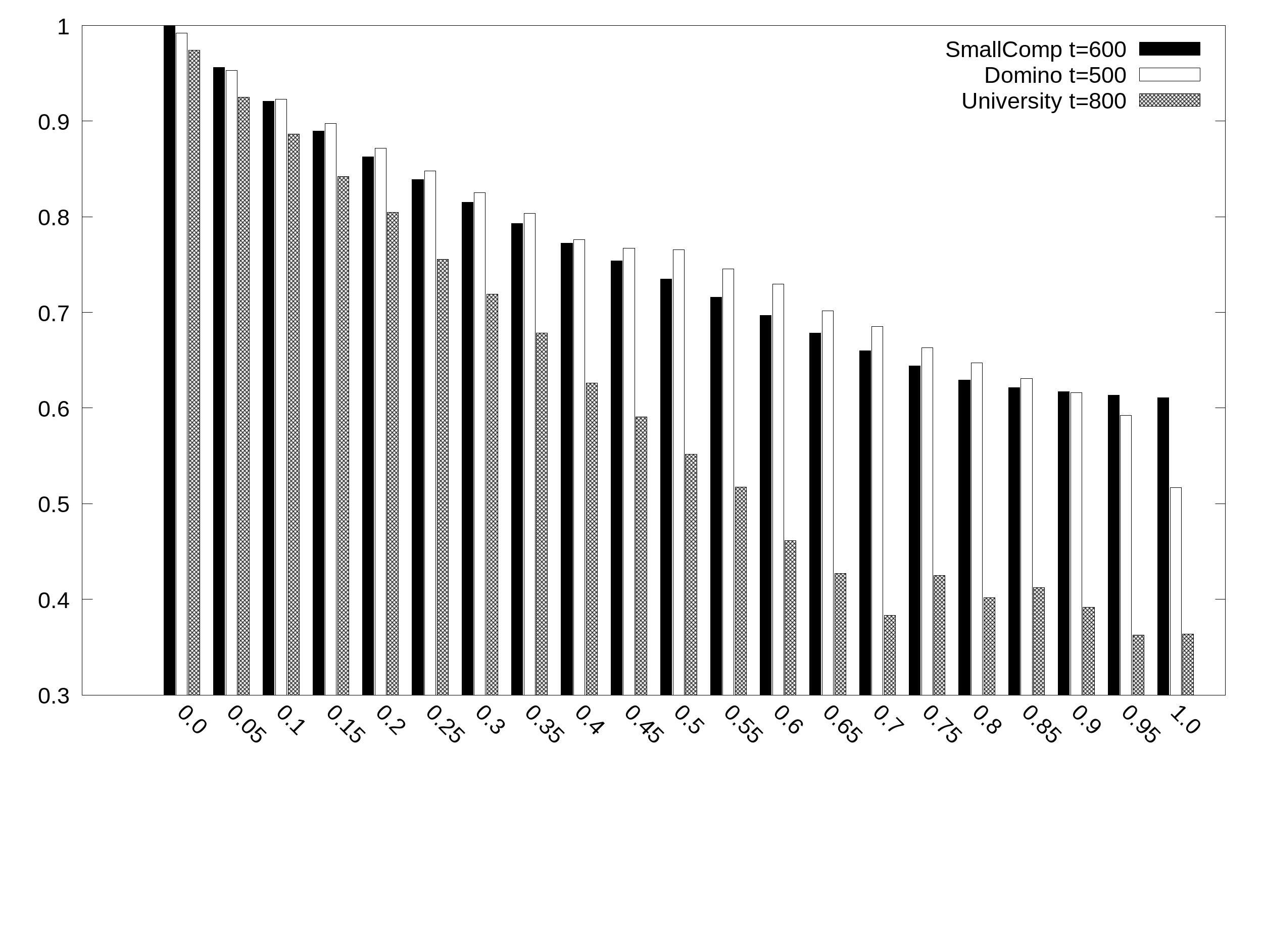
Time complexity based on Firewall1 variant
90 online fixing instances of increasing size have been generated from Firewall1 by selecting more and more of its users (i.e., rows); each instance is associated with a single exception to incorporate and generates a Max-SAT encoding of growing size.
| Number of users (CNF formula size) | UA | PA | exc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 users (0.3 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 21 users (5.1 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 37 users (11.3 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 53 users (27.5 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 69 users (54.9 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 85 users (79.6 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 101 users (120.1 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 117 users (162.4 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 133 users (231.7 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 149 users (300.9 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 165 users (337.2 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 181 users (380.7 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
| 197 users (519.1 MB) | UA | PA | exc |
The following figure shows the minimum timeout needed (y axis) to obtain a feasible solution for these inputs as a function of their size (x axis) with B=0.8.
Quality of incomplete solutions
Experiment based on SmallComp dataset to measure the ability of the incomplete solver adopted to satisfy the soft constraints. In particular, this is computed as the average weight of satisfied soft constraints over the total sum of weights for the 12 exceptions.
Average percentage of satisfied soft clauses (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x_axis) in the SmallComp dataset:
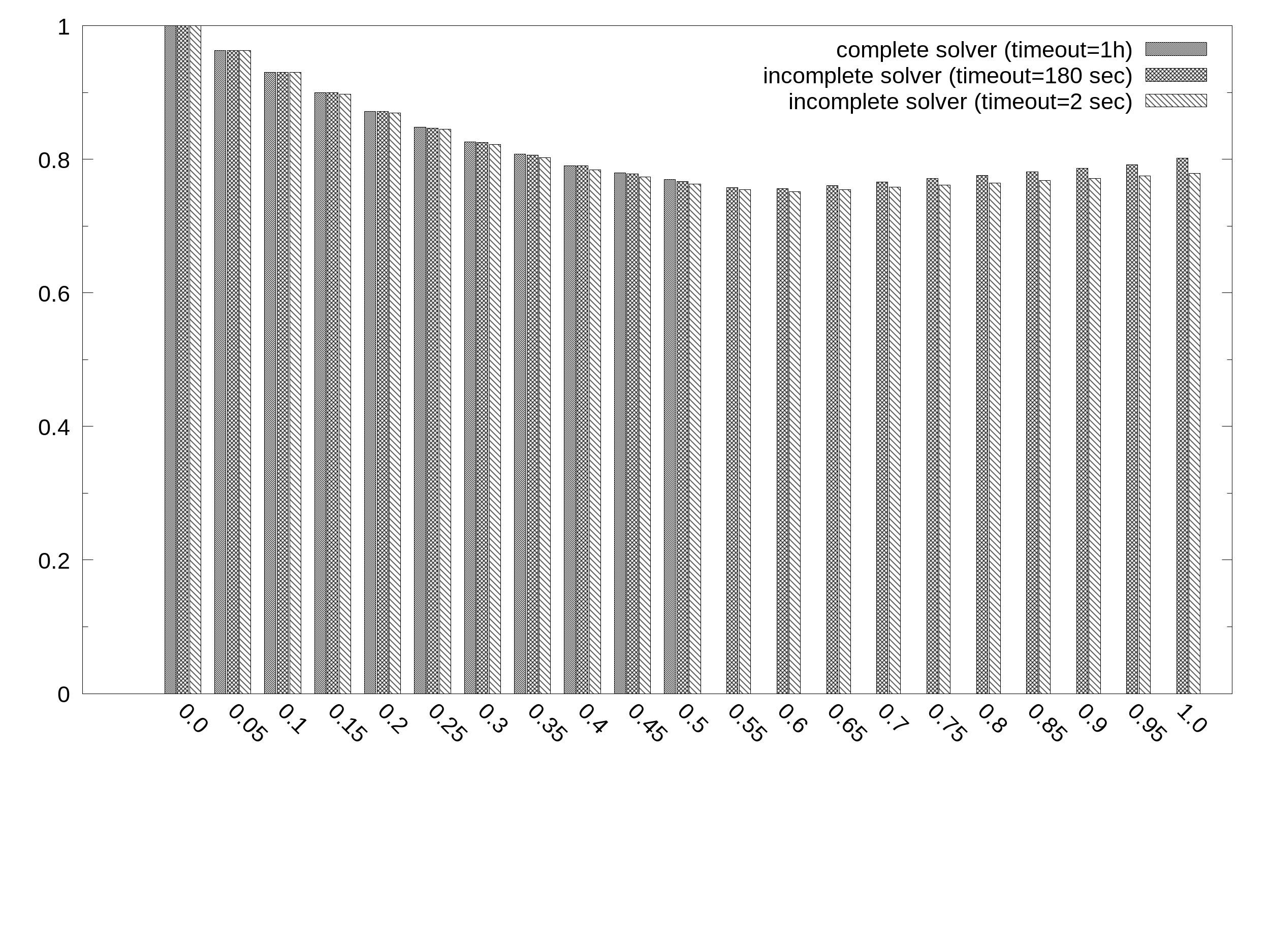
Results are also available in plain text in rates.txt which are based on the evalaution of the three configurations:
- complete solver Results_Complete.txt
- incomplete solver (timeout 2 sec) Results_t=2.txt
- incomplete solver (timeout 180 sec) Results_t=180.txt
Experimental Results: Single Exceptions/Violations
Impact of Beta
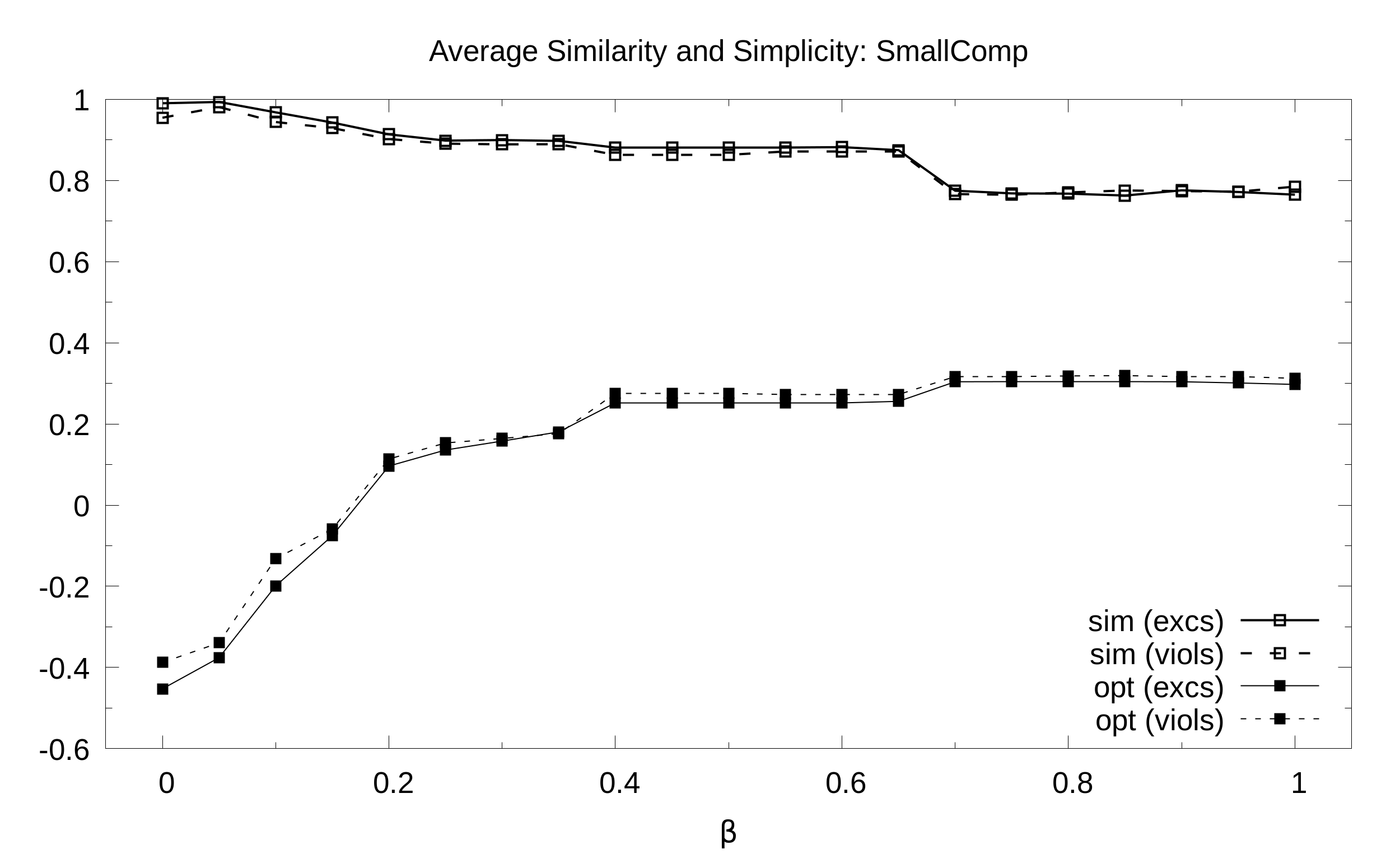
By adopting CCEHC Max-SAT solver we asses experimentally the impact of balance B to sim (similarity) and spt (simplicity) for three dataset. We considered both single exceptions and single violations to inlcude in the initial RBAC state.
Results for additions of exceptions
Results for removal of violations
SmallComp. Average simplicity and similarity (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
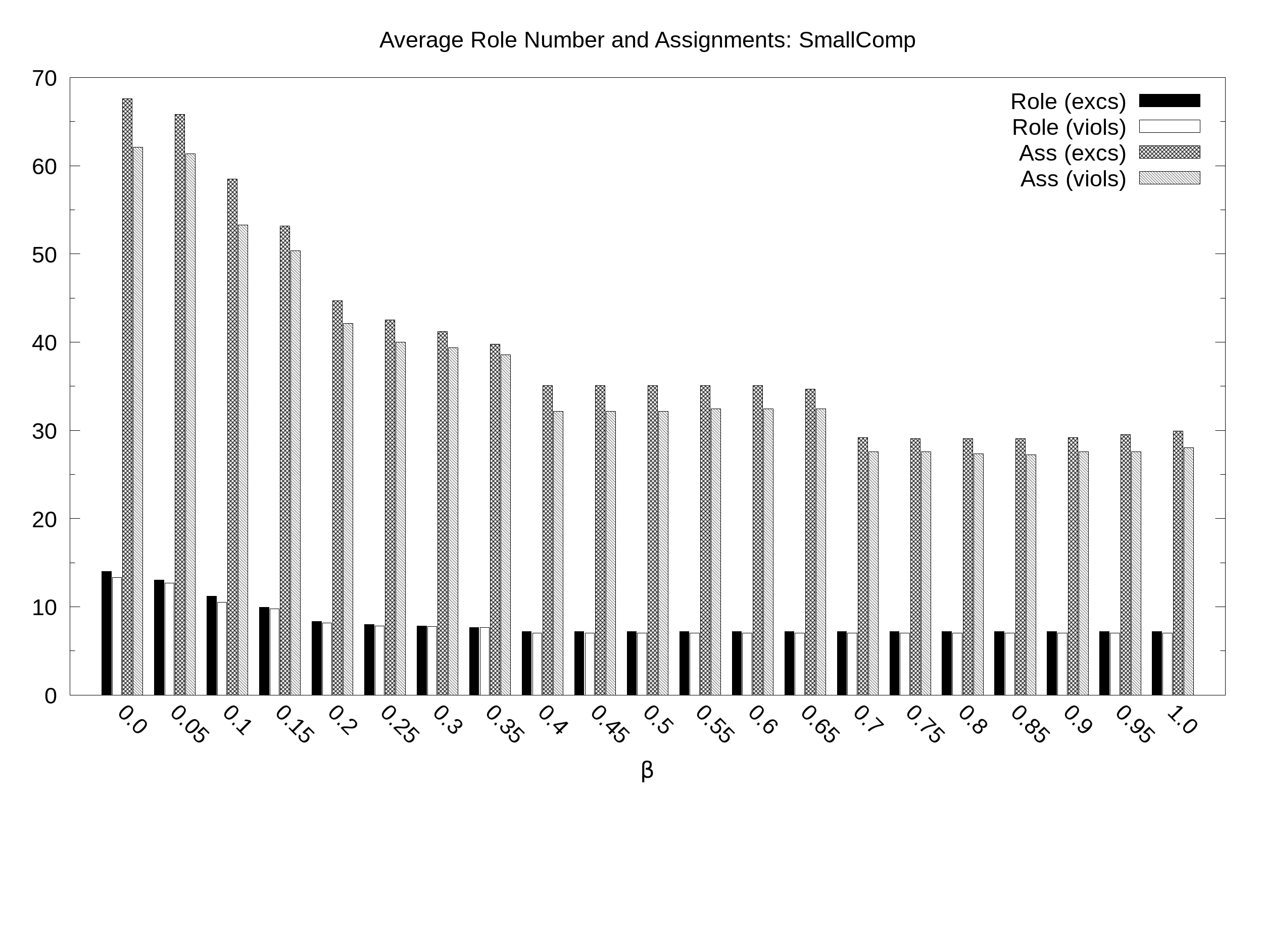
SmallComp. Average number of roles and assignments (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
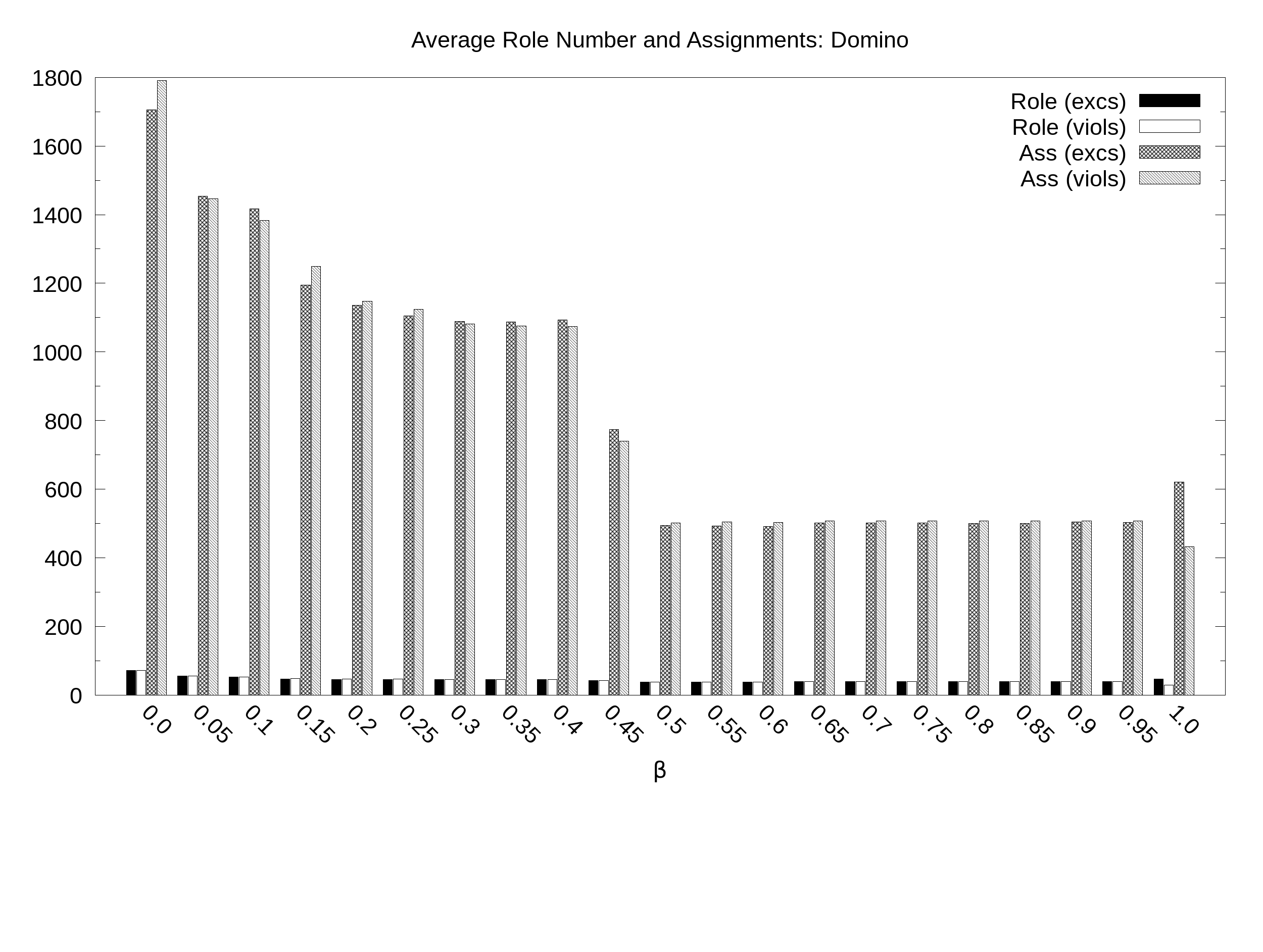
Domino. Average simplicity and similarity (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
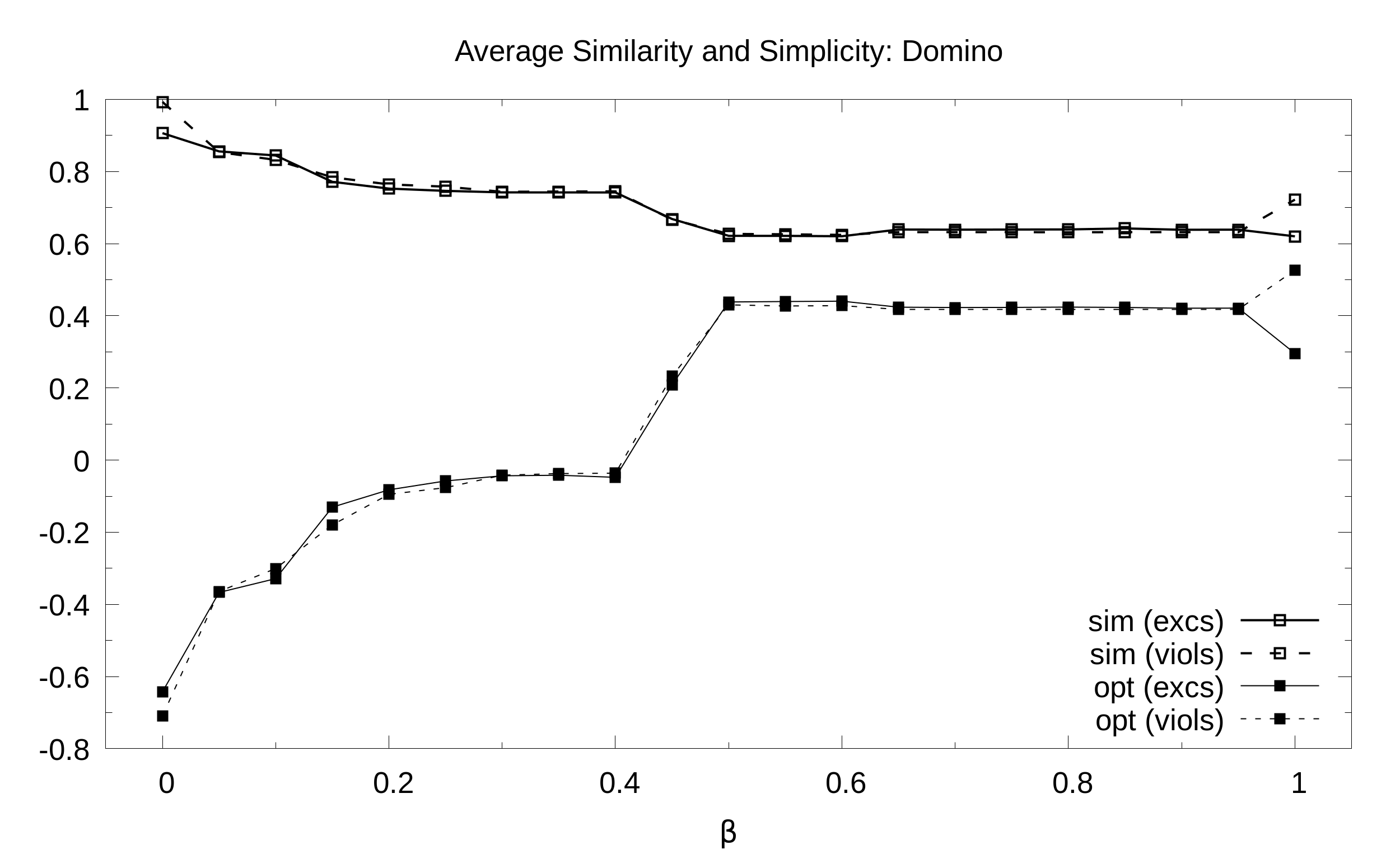
Domino. Average number of roles and assignments (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
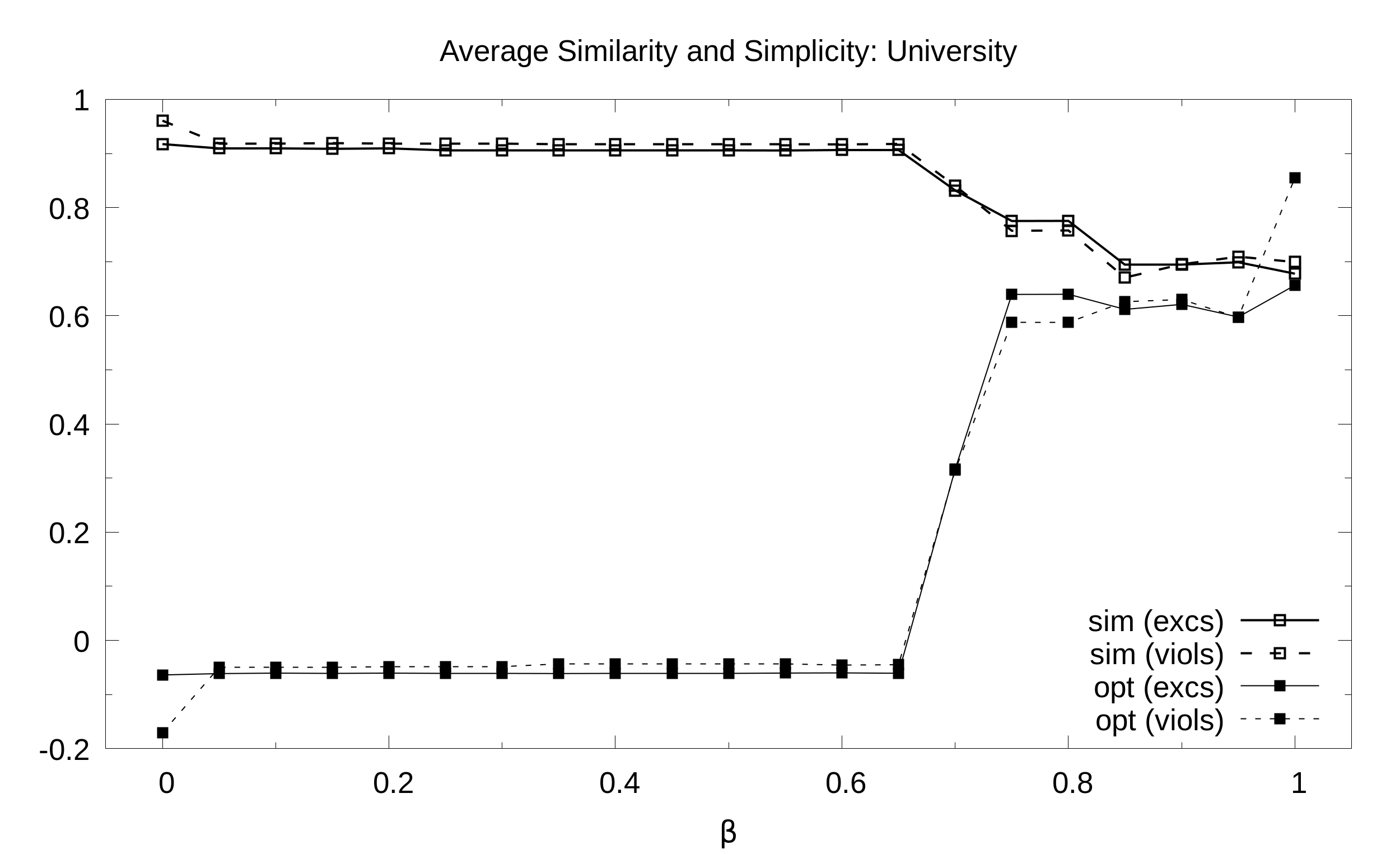
University. Average simplicity and similarity (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
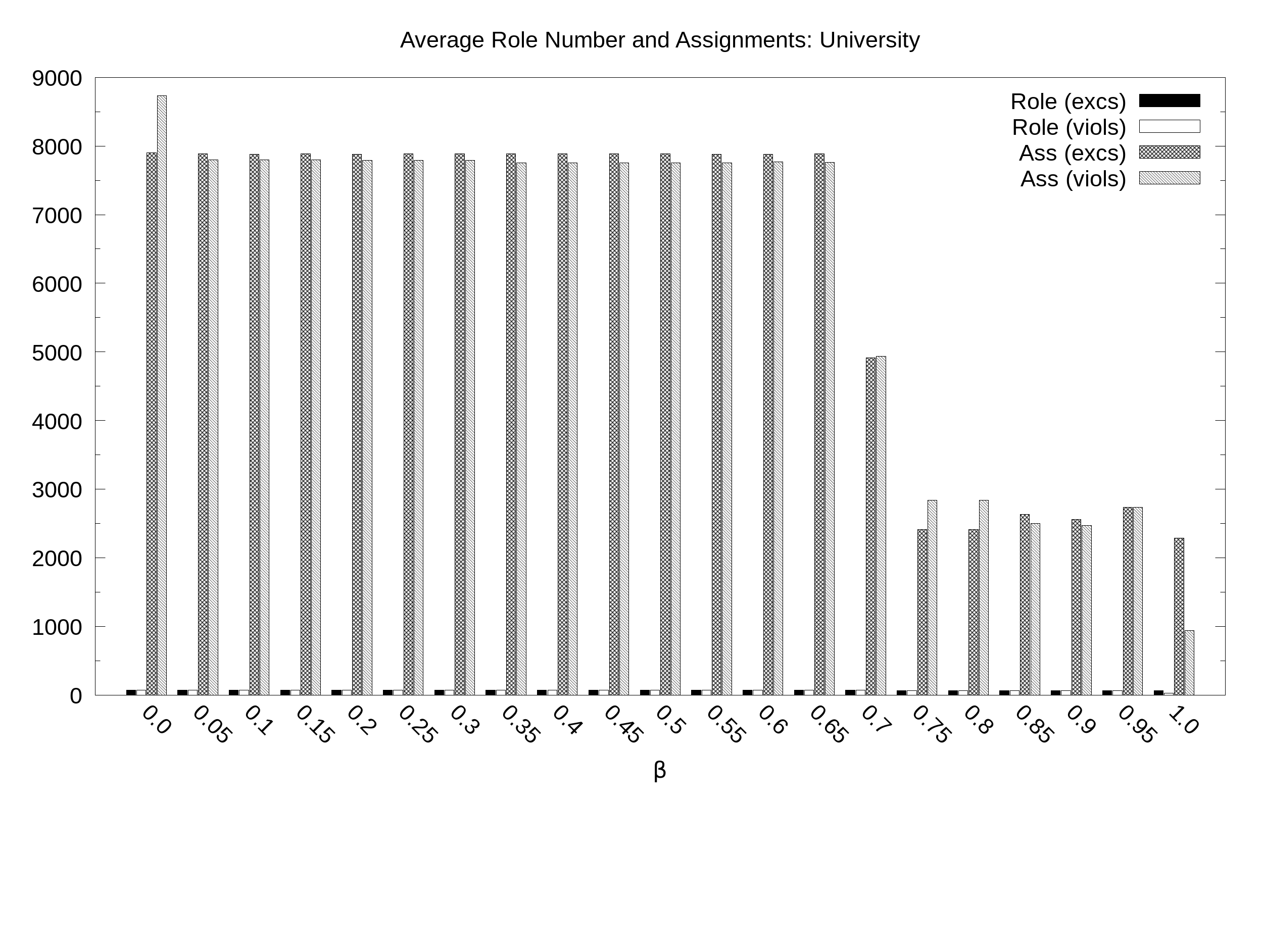
University. Average number of roles and assignments (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
Satisfied soft constraints. Average percentage of satisfied weights (y axis) depending on the balance B (x axis):
Impact of timeout
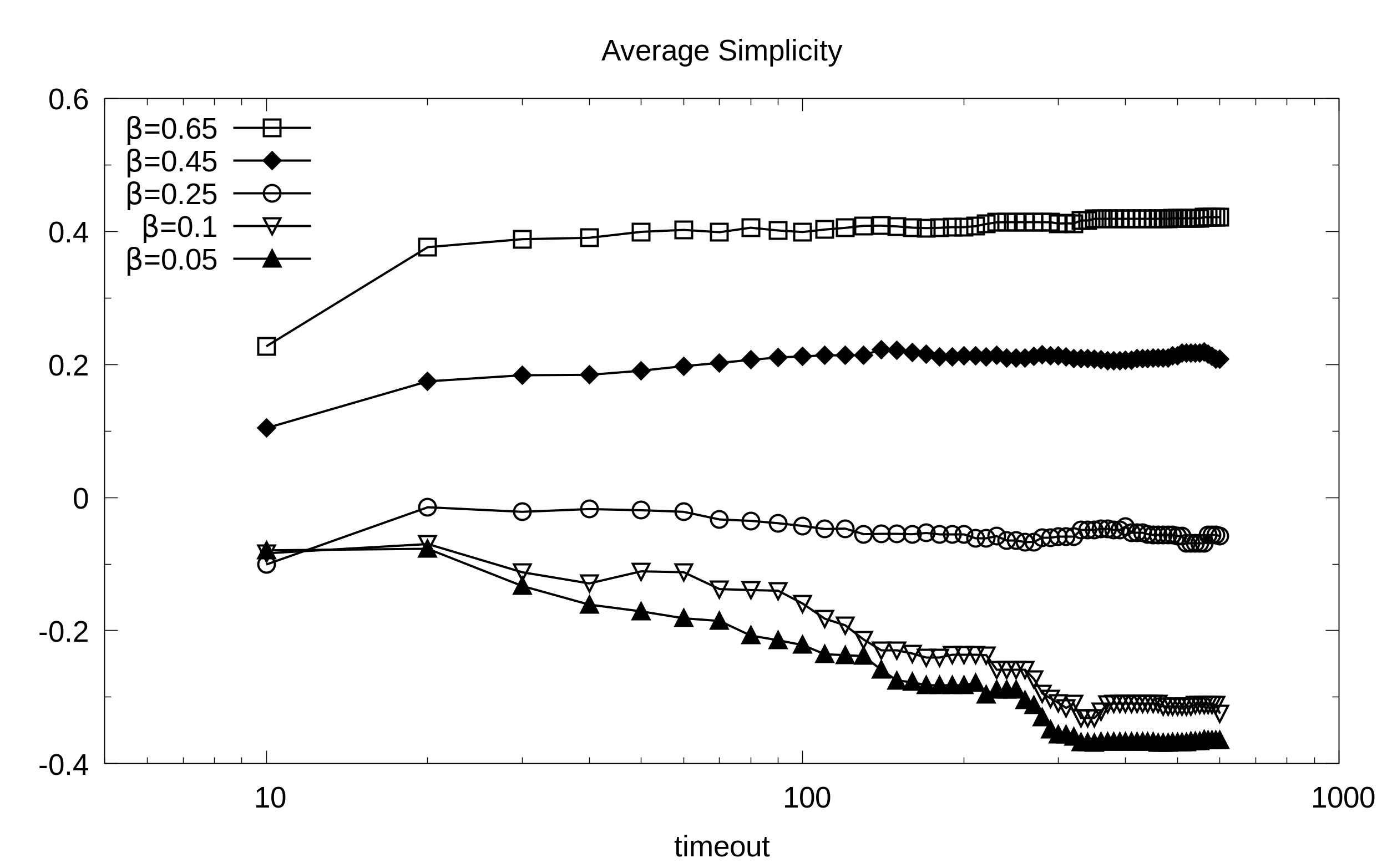
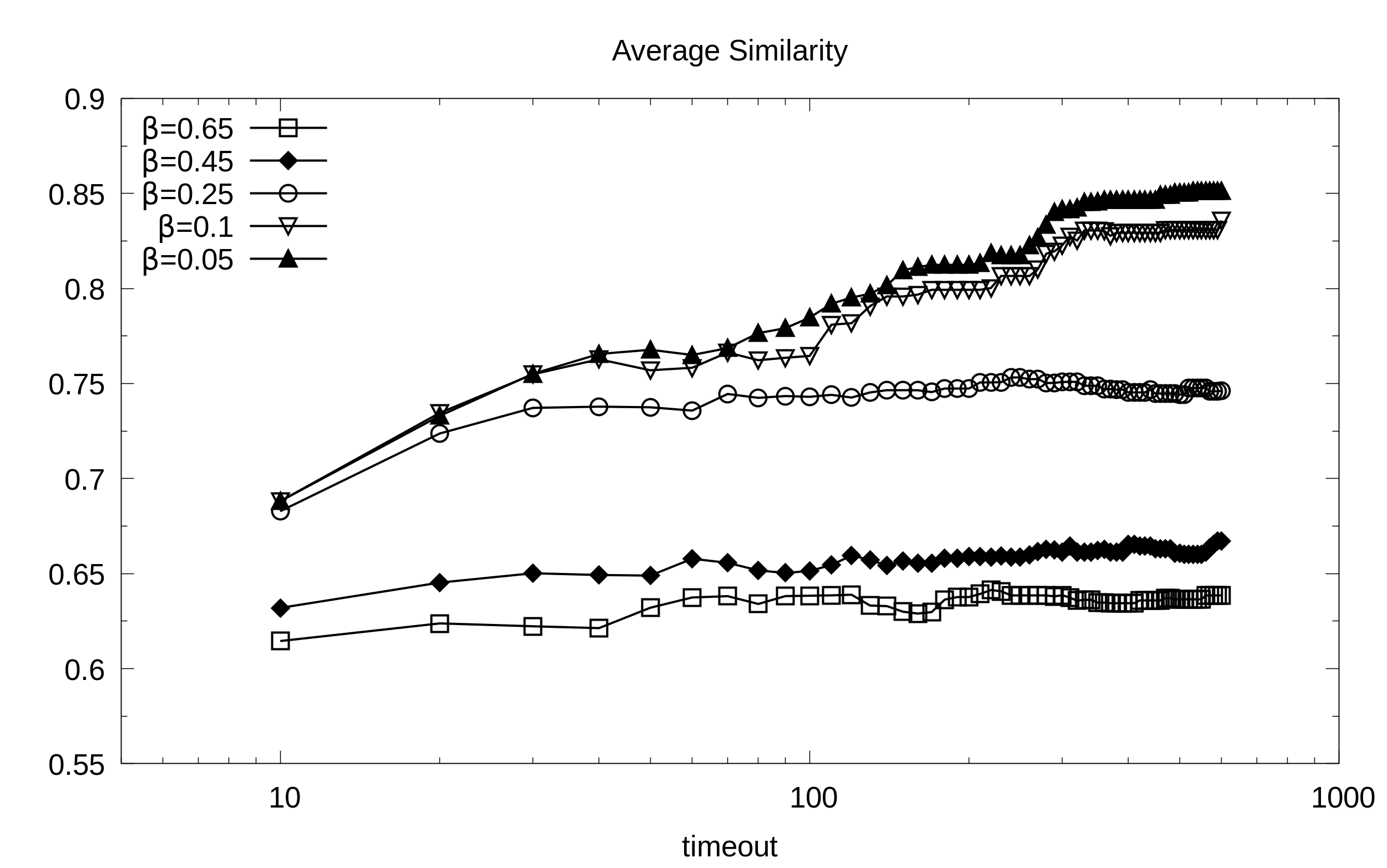
Results collected in the following are obtained starting from Domino to show the impact of the timeout with three different balance configurations:
Average simplicity in Domino (y axis) as a function of the timeout (x axis, secs) at different balance points B.
Average similarity in Domino (y axis) as a function of the timeout (x axis, secs) at different balance points B.
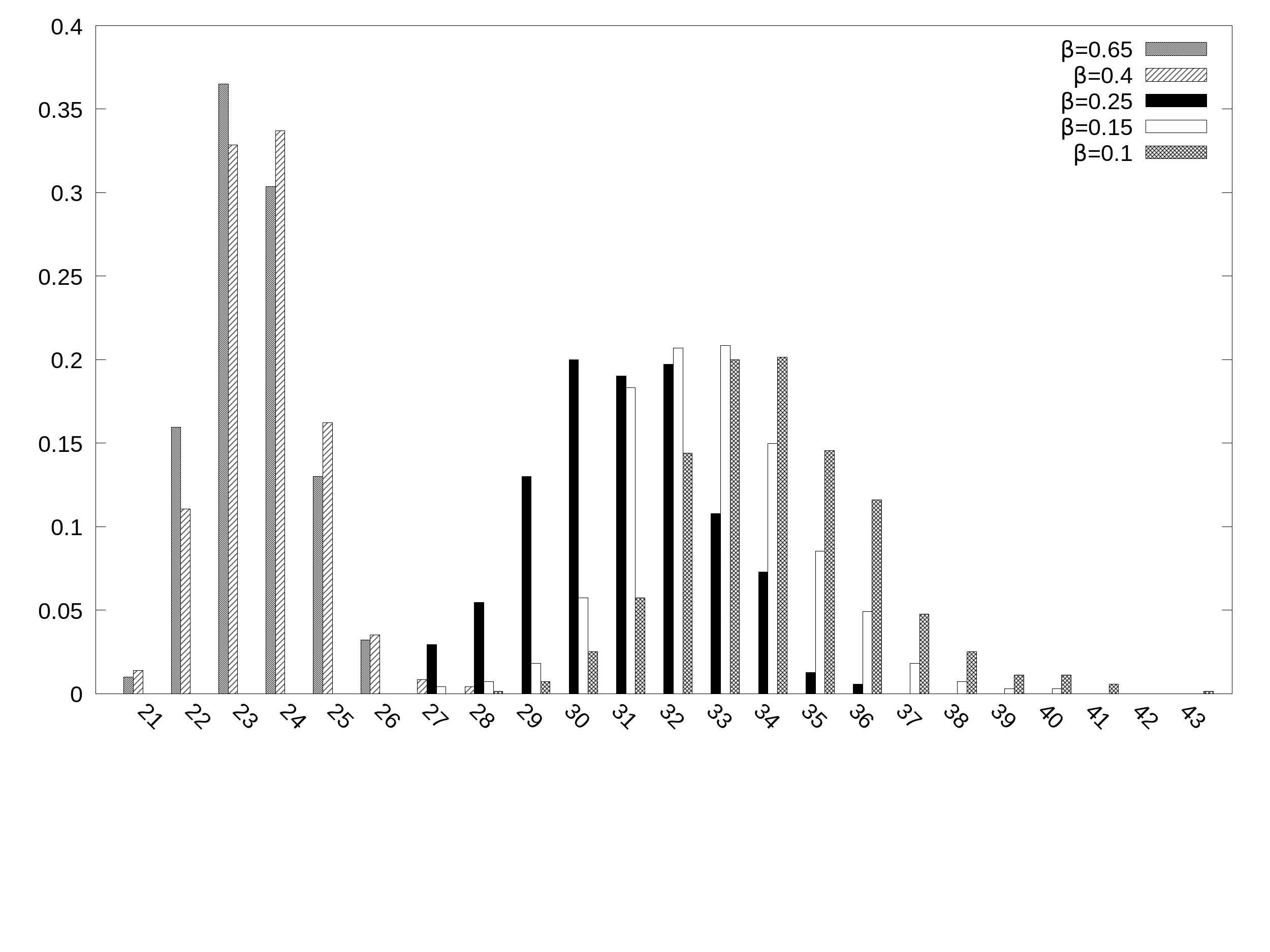
The order of exceptions with a variant of Domino dataset
We picked a string of 6 exceptions to be incorporated.
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
We generated all the 720 permutations as possibly different incorporating sequences. We fix each sequence and collected at each our metrics (715/720 paths considered as solvable in less than 60 seconds).
In the following is reported the distribution of the final number of roles obtained at different B values.
Corresponding input data are also available in the following:
Datasets for Comparison
These benchamrks have been adopted to compare our approach (RMS) with Fast Miner (FM) and Minimal Perturbation (MP) role mining algorithms. The initial RBAC state has been created with Pair Count role mining algorithm.
SmallComp
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
| Violation List | viols |
Domino
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
| Violation List | viols |
University
| Input | Link |
|---|---|
| Permission-to-User | UPA |
| User-to-role | UA |
| Permission-to-Role | PA |
| Exception List | excs |
| Violation List | viols |
Comparison Results
Solutions obtained for the above benchmarks by using FM, MP, and RMS (timeout=1200 sec) to perform RBAC maintenance tasks. For RMS, solutions are evaluate with 11 values of B sampled at regular intervals. Solutions are positioned according to their average simplicity (x axis) and similarity (y axis).
SmallComp
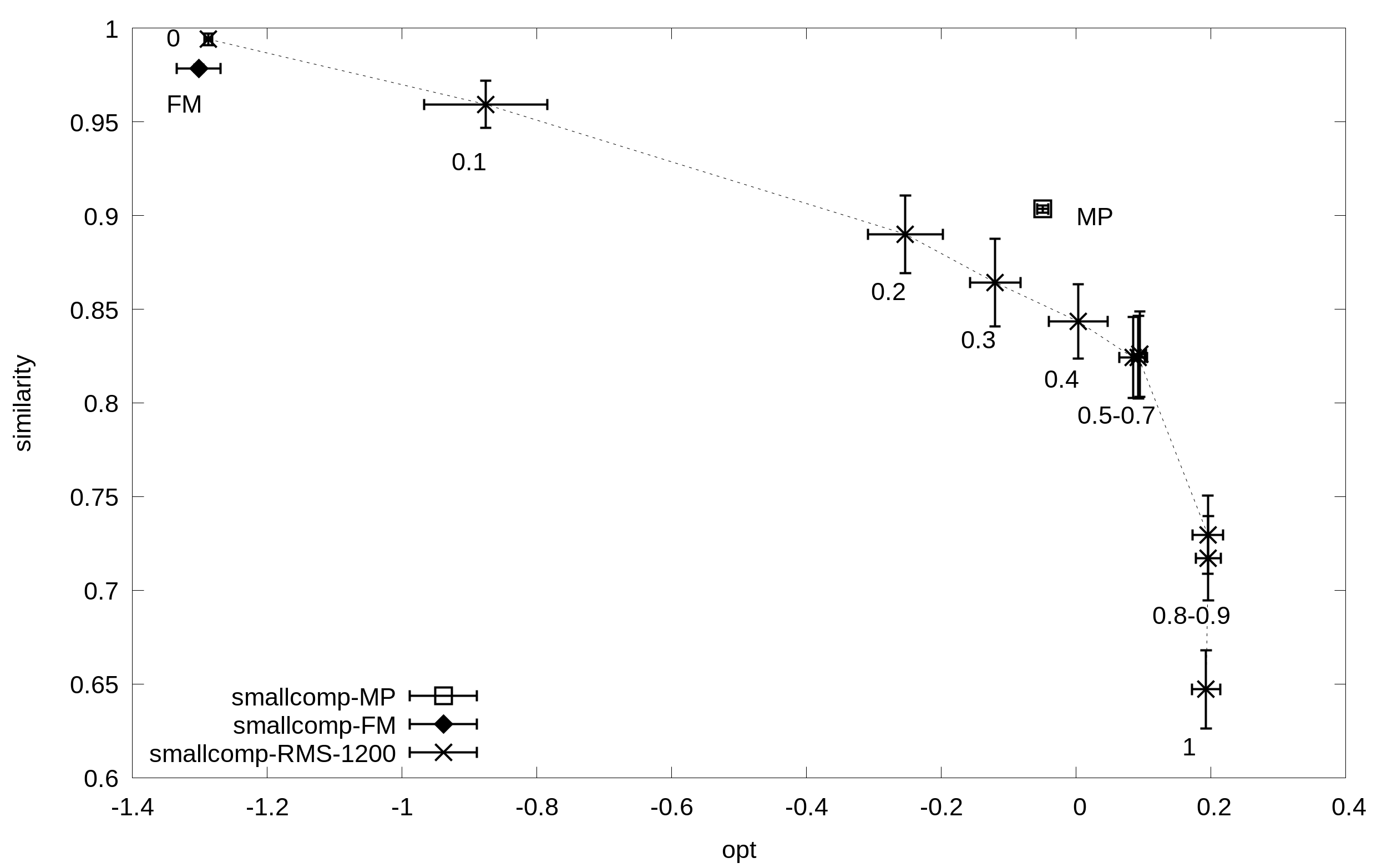
Corresponding input data are also available in the following:
Domino
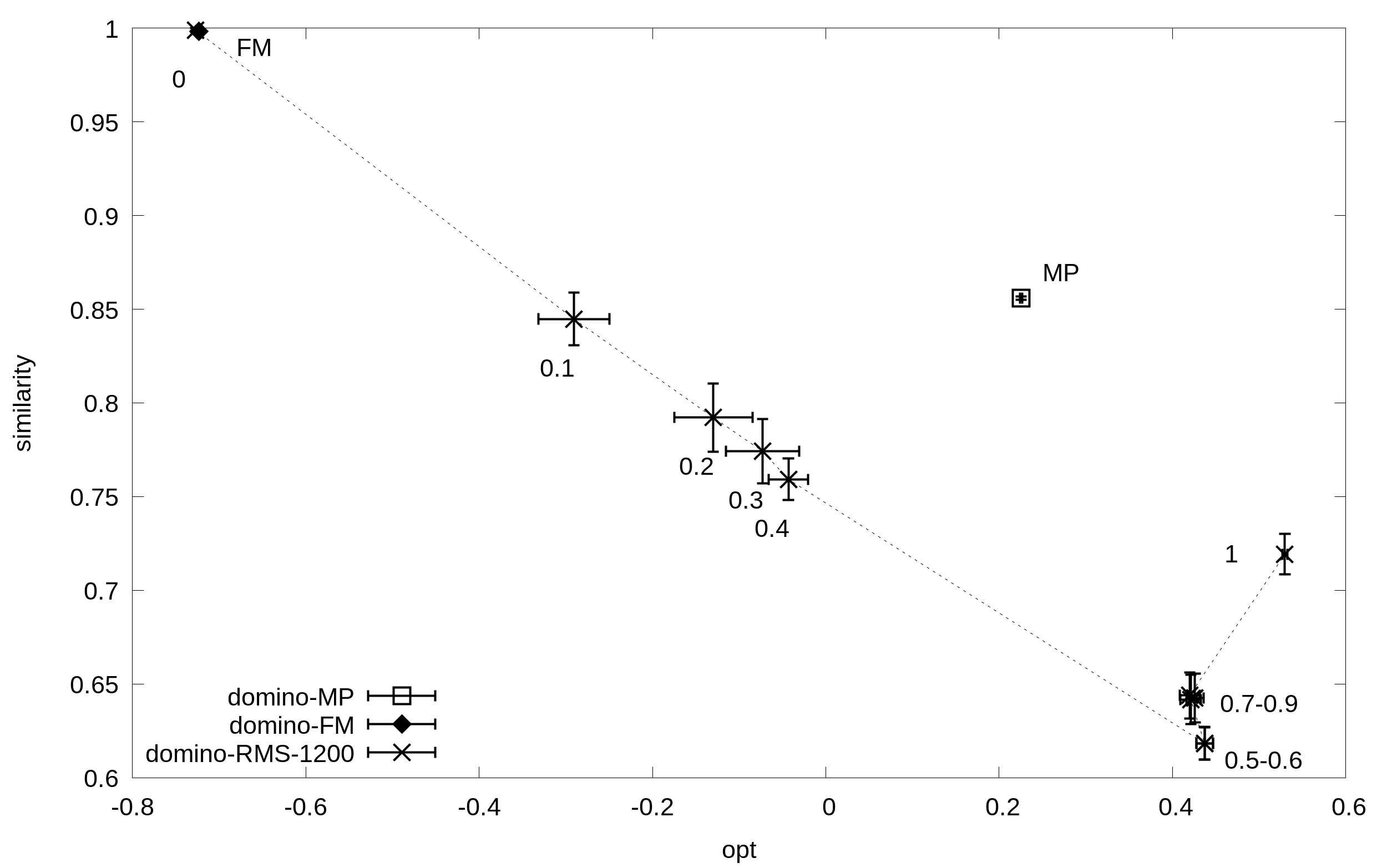
Corresponding input data are also available in the following:
University
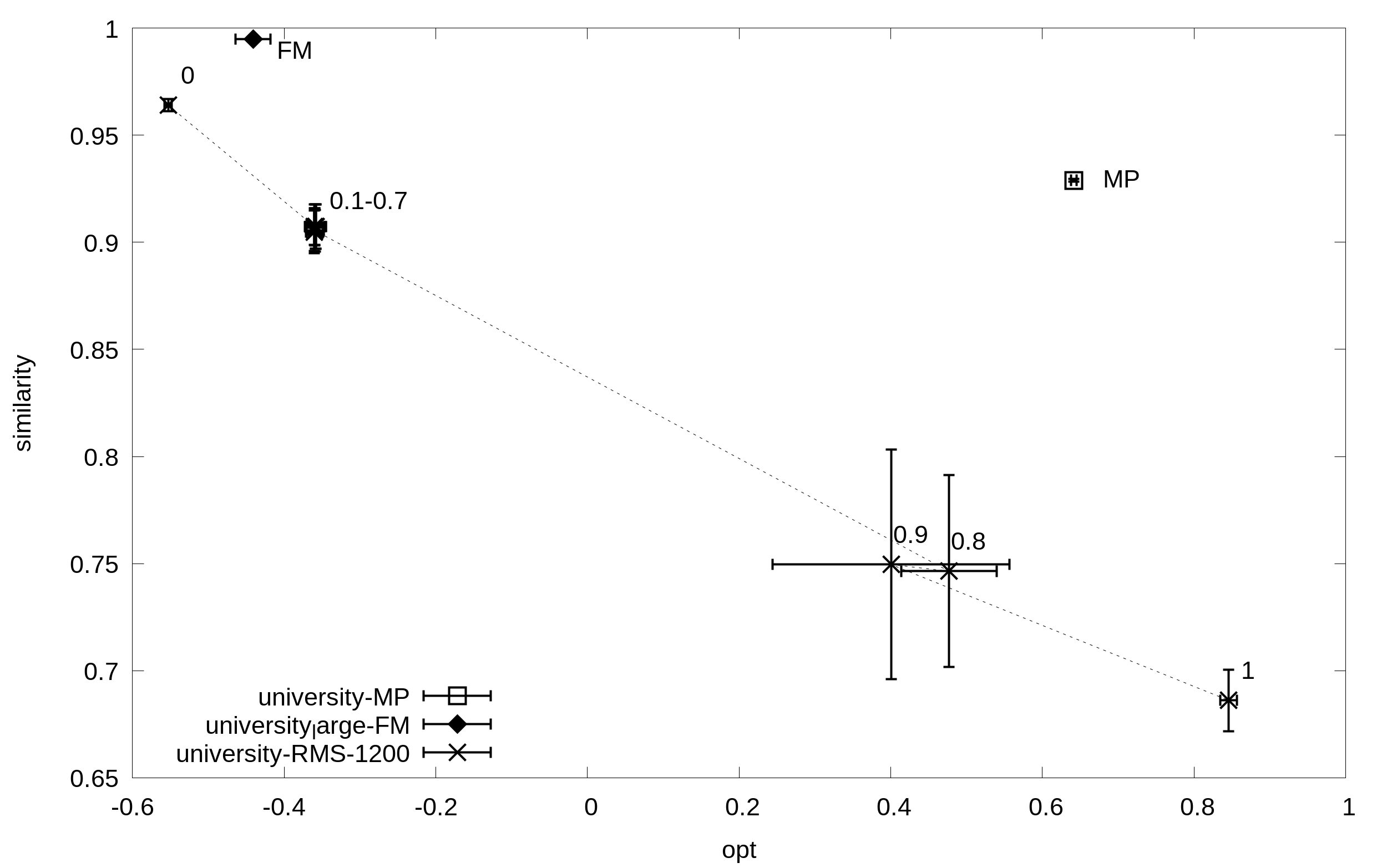
Corresponding input data are also available in the following:
Datasets: Multiple Exceptions/Violations
These benchmarks have been adopted to prove the ability of our algorithms in including lists of exceptions and violations in one single step. Sequences of exceptions and violations (10 runs) have been pseudo-randomly generated according to a specific Markov chain model.
SmallComp
| Run | UA | PA | Excs | Viols |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 1 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 2 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 3 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 4 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 5 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 6 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 7 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 8 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 9 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
Domino
| Run | UA | PA | Excs | Viols |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 1 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 2 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 3 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 4 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 5 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 6 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 7 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 8 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 9 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
University
| Run | UA | PA | Excs | Viols |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 1 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 2 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 3 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 4 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 5 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 6 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 7 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 8 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
| 9 | UA | PA | excs | viols |
Experimental Results: Multiple Exceptions/Violations
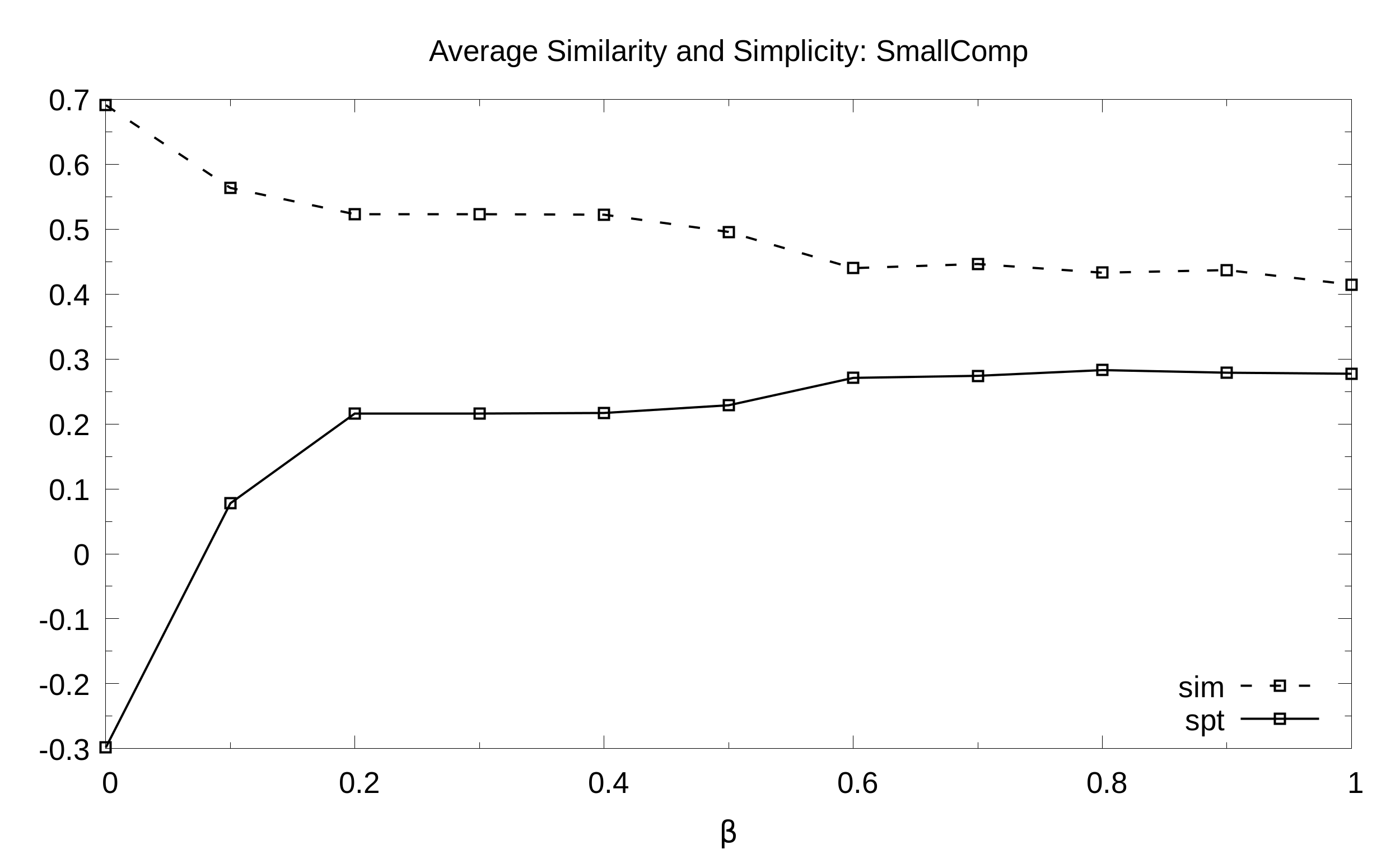
Here we asses experimentally multiple exceptions and multiple violations in one single problem instance. We evaluate the impact of balance B to sim (similarity) and spt (simplicity) for three dataset.
Results for addition/removal of multiple exceptions/violations
SmallComp. Average simplicity and similarity (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
Domino. Average simplicity and similarity (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
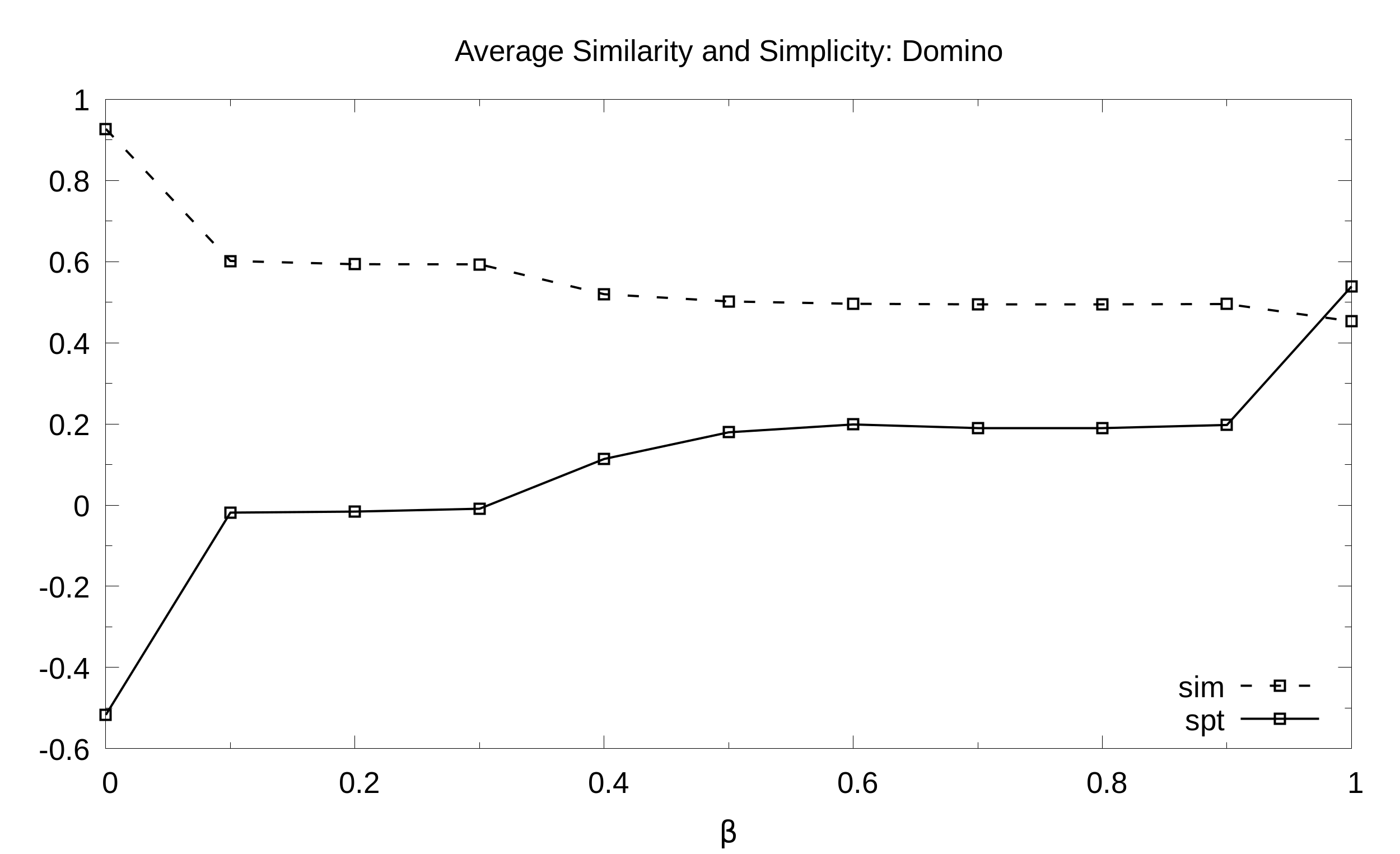
University. Average simplicity and similarity (y axis) as a function of the balance B (x axis) with 21 values of B sampled at regular intervals:
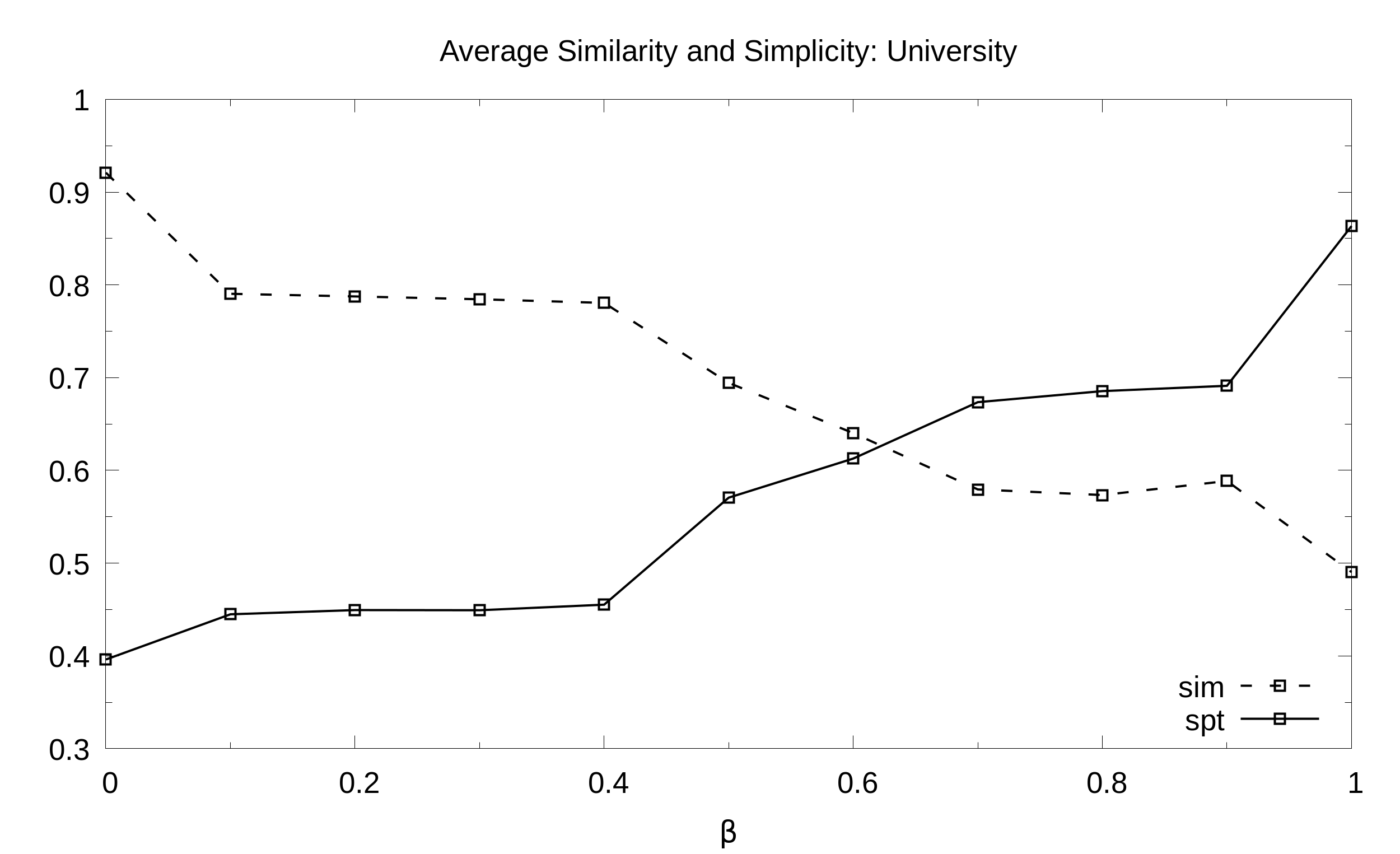
Datasets: Planning
These benchmarks have been adopted to prove the ability of our algorithms in generating maintenance plans to include sequences of violations. The latter (10 runs) have been pseudo-randomly generated according to a specific Markov chain model. In the following, (I/O) stands for (Input PDDL problem/Output plan)
SmallComp
| Beta/Run | Run 0 | Run 1 | Run 2 | Run 3 | Run 4 | Run 5 | Run 6 | Run 7 | Run 8 | Run 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta 0.0 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.05 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.1 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.15 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.2 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.25 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.3 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.35 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.4 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.45 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.5 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.55 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.6 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.65 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.7 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.75 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.8 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.85 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.9 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.95 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 1.0 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
Domino
| Beta/Run | Run 0 | Run 1 | Run 2 | Run 3 | Run 4 | Run 5 | Run 6 | Run 7 | Run 8 | Run 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta 0.0 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.05 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.1 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.15 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.2 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.25 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.3 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.35 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.4 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.45 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
| Beta 0.5 | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O | I/O |
Experimental Results: Planning
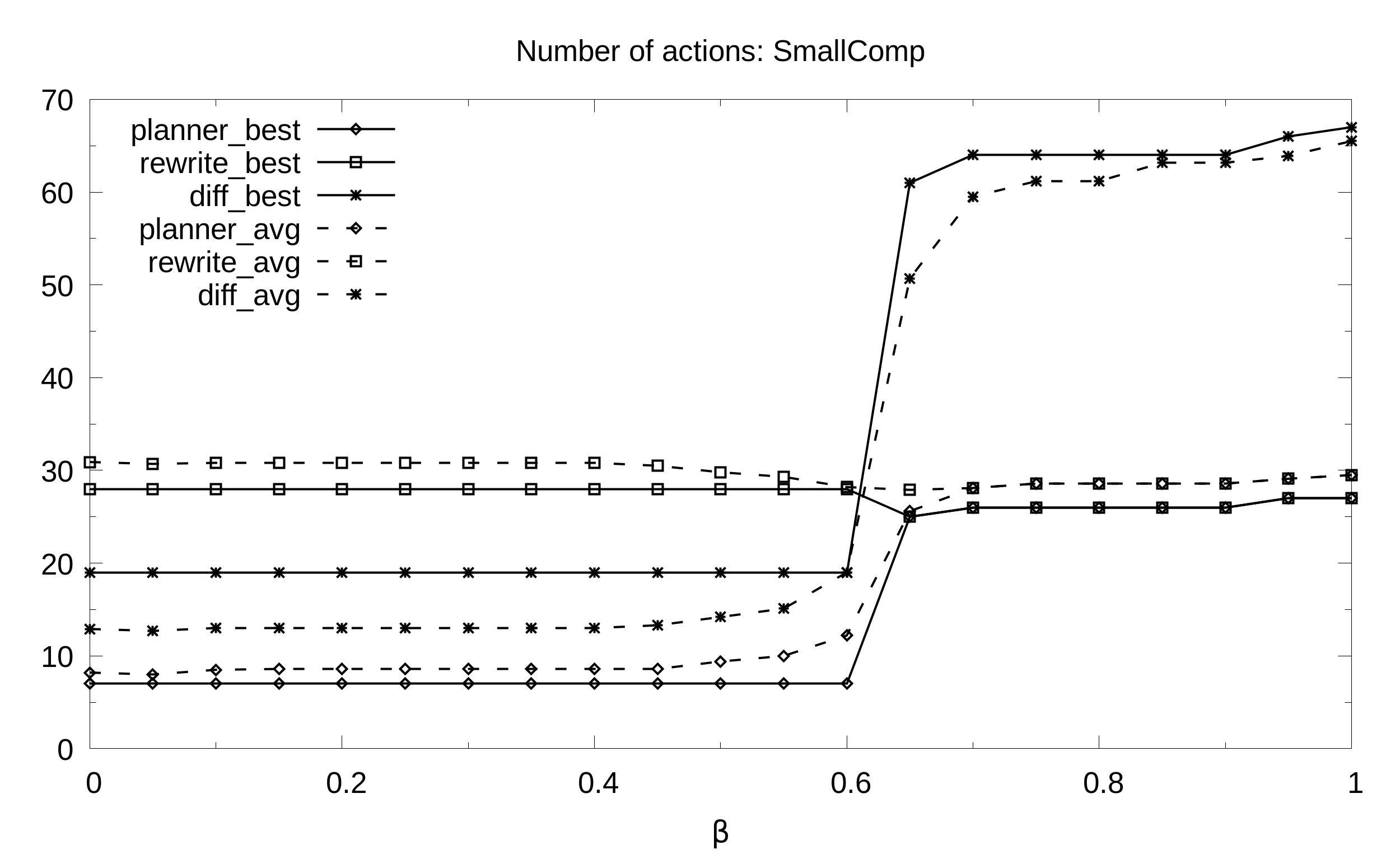
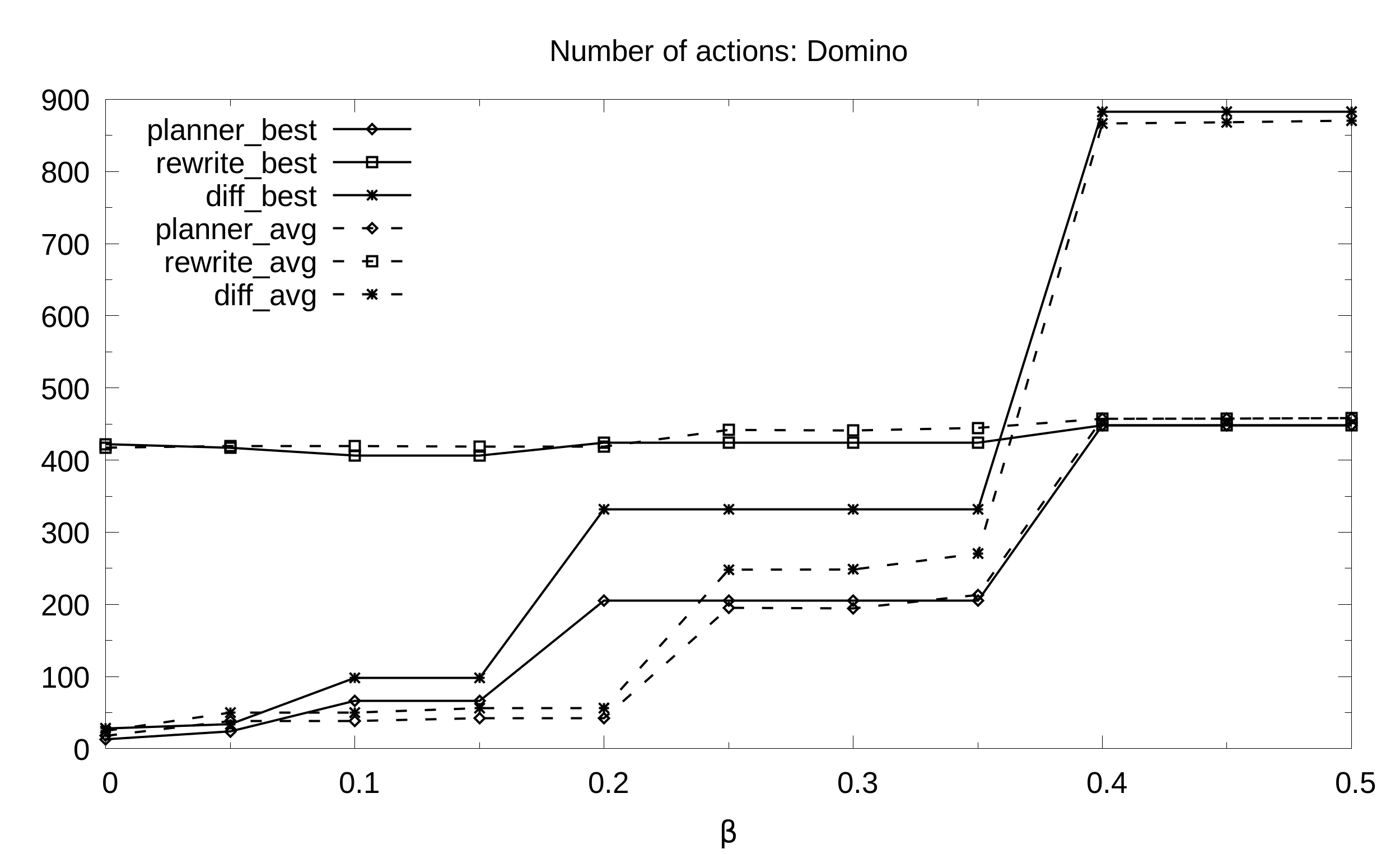
Here we evaluate the quality of the maintenance plans (shortness) generated with our algorithms. We compared our results with two baselines: rewrite which erases the input RBAC state to build from scratch the target state; diff which adjusts the differences between target and input states.
SmallComp. Average and best number of actions (y axis) as a function of the balance beta (x axis) for multiple pseudo-randomly generated violations:
Domino. Average and best number of actions (y axis) as a function of the balance beta (x axis) for multiple pseudo-randomly generated violations:
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Images have been created by the means of a software with non-commercial license.
We are currently setting up a git-hub repository to host the “RBAC Maintance” Open Source software. Meanwhile we are available to distribute it upon reception of a simple request of interest sent to “Anonymous Mail”